2024.02.16
Vibration and Noise Decoded: How to Precisely Identify Gearbox Issues?

Vibration and noise usually have a mutually dependent positive relationship, where typically, the greater the vibration, the louder the accompanying noise, and vice versa. How can we determine whether a gearbox is functioning normally based on the sound it emits? Initially, we can judge by whether the sound produced by the gearbox is regular or irregular. Listen carefully to determine if the noise has a pattern; if there is a consistent sound, that indicates normal operation. Generally, this sound is considered normal. However, if the noise is too loud or the sound pattern is irregular, it certainly indicates an issue within the gearbox.
Methods for Handling Abnormal Vibrations:
|
Cause and phenomenon |
Solution |
|
Poor installation: Motor bolts are loose Shaft deformation and imbalance Coupler damage |
Readjust poorly installed components and tighten bolts. 1. Gearbox and motor connection is not perpendicular, causing resonance; needs re-installation adjustment. 2. Output shaft connected to the gearbox is bent or deformed; check coaxiality of the output transmission shaft. 3. Equipment transmission shaft and gearbox center height are inconsistent; adjust the gearbox mounting surface to ensure both dimensions are equal. |
|
Insufficient Mounting Strength: Equipment base screws or other fixing screws are loose. |
Strengthen the mounting base. |
|
Bearing damage: Friction exists between transmission parts or mounting base and bearings, leading to vibrations if bearings are damaged or poorly lubricated. |
Although bearing metal has good hardness, it lacks impact resistance and fatigue resistance, and cannot recover after deformation. Therefore, bearings must be replaced if there are signs of damage. |
|
Gear faults: Gears can easily wear out over time. If gear surfaces have pits, cracks, or other issues, it can cause vibrations. Certain gaps exist between gears; excessive gaps or loose assembly between gears and bearings can cause vibrations. |
Inspect gear condition and replace faulty gears. |
|
Poor Machining Precision: The machining precision of the gearbox itself or its components is insufficient, leading to noise and impact during gear engagement due to uneven load distribution. |
Replace faulty components. |
|
Vibration Source or External Impact Interference: Gearboxes are often installed in complex machinery that may have inherent vibration sources, causing interference and vibration. Gearboxes can be affected by external impact forces, such as machine vibrations, impacts, etc., causing vibrations. |
Install the gearbox properly to avoid external environmental impacts and avoid overloading during use. |
|
Overloading Overloading the gearbox can cause excessive pressure, leading to vibrations. |
Through regular or daily inspections, check if gears, bearings, and other components show early signs of damage or excessive wear, and replace or repair them timely. |
|
Poor Lubrication: Gearboxes require regular lubrication; poor lubrication or the use of inappropriate lubricants can cause vibrations. |
Enhance gearbox lubrication management, select the appropriate lubricant, and regularly replace and clean the lubrication system. |
Abnormal Vibration Handling Methods:
Cause and Phenomenon | Solution
Poor Installation:
- Motor bolts loose.
- Shaft deformation causing imbalance.
- Coupler damage. | Re-adjust if poorly installed and tighten bolts.
1. Gearbox and motor connection not perpendicular, causing resonance, requires re-installation adjustment.
2. Output shaft connected to gearbox bent or deformed, need to check coaxiality of the output transmission shaft.
3. Equipment transmission shaft and gearbox center height inconsistency, need to adjust gearbox mounting surface to ensure equal installation dimensions.
Insufficient Base Strength:
- Equipment foundation bolts or other fixing screws loose. | Strengthen the base.
Bearing Damage:
- Friction between transmission parts or base and bearings, leading to vibration if bearings are damaged or poorly lubricated. | Bearings, despite their hardness, lack impact resistance and fatigue resistance, and cannot recover after deformation, so they must be replaced if there are signs of damage.
Gear Wear:
- Gears prone to wear over long operation, causing vibration if gear surfaces have pits, cracks, etc.
- Gaps between gears, if too large or gear and bearing assembly not tight, leading to vibration. | Inspect gear condition, replace defective gears.
Poor Machining Precision:
- Gearbox's machining precision and related components not sufficient, leading to uneven load distribution, noise, and impact during gear engagement. | Replace defective components.
Vibration Source or External Impact Interference:
- Gearboxes often installed in complex machinery with inherent vibration sources, causing interference and vibration.
- Gearboxes subject to external impacts, like machine vibration, impacts, etc., causing vibration. | Properly install gearbox to avoid external environmental impact, avoid overloading during use.
Overload:
- Overloading gearbox causes excessive pressure, leading to vibration. | Regularly inspect gearbox gears, bearings, etc., for premature damage or excessive wear, and replace or repair promptly.
Poor Lubrication:
- Gearboxes need regular lubrication; poor lubrication or unsuitable lubricant causes vibration. | Enhance gearbox lubrication management, select suitable lubricant, replace and clean the lubrication system regularly.
Precautions:
When handling abnormalities, prioritize personal safety to prevent accidents. If vibration is severe, non-maintenance personnel should retreat to a safe area to prevent accidents. If equipment failure is detected, immediately stop using the equipment, inspect it, confirm the cause of the failure, and repair it. If the failure is not due to the equipment, inspect machine parts for wear or looseness, and try adjusting the installation settings. If wear or looseness is found, replace or repair the corresponding parts.
Case Study:
Abnormal Phenomenon
a. Intermittent noise at 1200rpm and significant, piercing noise at 3000rpm during motor test run.
b. Disassemble gearbox to check for gear anomalies.
c. Found one planetary gear damaged, refer to (Figure 1) for replacement.
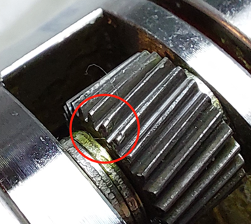
Maintenance Handling
Upon inspection, found planetary gear with impact damage. After replacing the planetary gear, no noise during test run, replaced gear oil, and new O-rings. Refer to (Figure 2) for noise level before maintenance, and (Figure 3) for noise level after maintenance.

Summary:
Vibration in gearboxes is a common issue that arises from a variety of causes and requires a comprehensive approach to address. By enhancing the management and maintenance of equipment and promptly addressing issues, the normal operation of gearboxes can be ensured, extending the lifespan of the equipment and improving production efficiency.
If you encounter any problems with your gearbox, or have any challenging issues, please feel free to contact us at any time. Let us have the opportunity to solve your problems. You are welcome to call or email GearKo for assistance.