2023.10.27
Equipment Maintenance Manual: How to Diagnose and Fix Common Problems

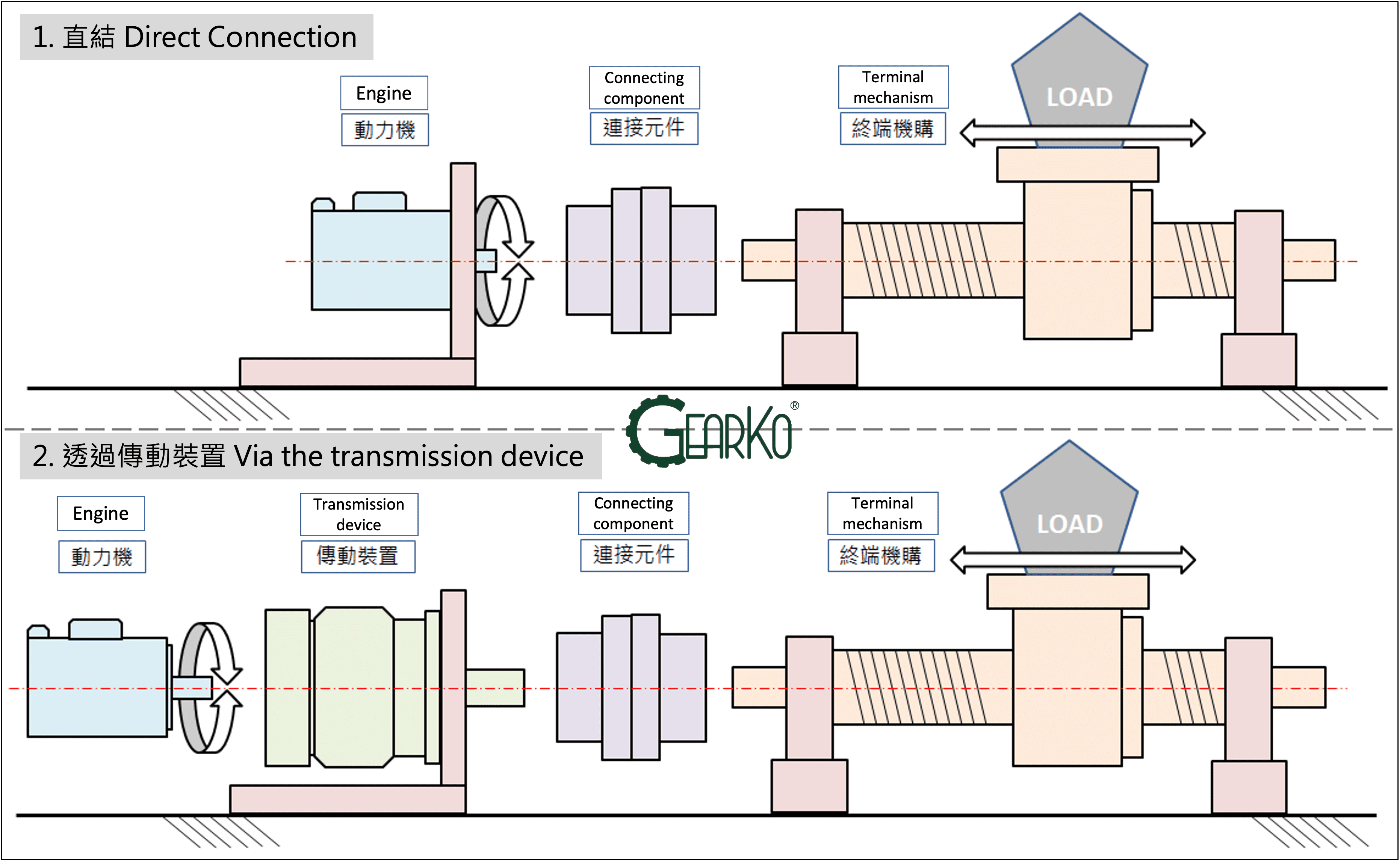
Before diving into the analysis, let's first understand the components that make up the production equipment. The transmission module of general production equipment, from input to output, changes rotational motion into linear motion or other motion trajectories. Most often, they follow one of the two sequences listed below, as illustrated in Figure 1:
Direct connection: Power input → Connecting component → Terminal mechanism output
Through transmission devices: Power input → Various transmission devices → Connecting component →Terminal mechanism output
Glossary:
- Engine: Generally refers to prime movers, such as: electric motors, internal combustion engines, etc., devices that can utilize energy to produce power.
- Transmission device: Can change or transmit the energy or direction of motion, like various gear reducers, ball screws, slides, etc.
- Connecting components: Transfer power to the actuating mechanism, such as: couplings, gears, gear racks, sprockets, chains, timing belts, timing pulleys, etc.
- Terminal mechanism: The final mechanism that can meet work conditions, such as making heavy objects move linearly or rotate.
Next, we'll briefly list five common anomalies, analyze their possible causes, and discuss methods to eliminate them. Please refer to Table 1 below.
|
Anomaly Condition |
Category |
Possible Cause |
Method of Elimination |
|
1.End mechanism not operating |
Equipment unloaded |
Power Supply Failure. |
Verify main equipment power connectivity. |
|
Wire Breakage. |
Conduct wire inspection. |
||
|
Switch Contact Problem. |
Proceed with repair or replacement. |
||
|
Motor Coil Breakage. |
Send to specialist for repair. |
||
|
Three-phase Motor Connected to Single-phase Voltage. |
Verify voltage and wiring configuration. |
||
|
Single-phase Motor Without Capacitor. |
Connect capacitor. |
||
|
Single-phase Motor Starter Malfunction. |
Send to a professional manufacturer for repair. |
||
|
Issue in one of the following: Power Machine, Transmission Device, Connection Component, Terminal Mechanism. |
Segment-check each mechanism's operation and verify tightness of fastening screws. If necessary, disassemble to inspect bearings, gears, slide rails, sliders, and other transmission components. If unresolvable, contact the manufacturer. |
||
|
Equipment Loading |
Low voltage. |
Check if the power line is too long or too thin, resulting in insufficient voltage or current. |
|
|
Overload operation. |
Remove the load and then run a test. |
||
|
Shaft key destroyed. |
Send to a professional manufacturer for repair. |
||
|
One of the mechanisms in the power machine, transmission device, connecting element, or terminal mechanism malfunctions. |
Check each mechanism's operation and whether the fastening screws are loose in sections. If necessary, disassemble to verify if bearings, gears, slide rails, sliders, etc., are functioning properly. If unable to handle in-house, contact the manufacturer. |
||
|
2. Device Overheating |
Engine |
Overloaded operation. |
Reduce the operational load to recommended levels. |
|
Frequent startups and shutdowns. |
Kindly reduce the frequency of use to maintain device longevity. |
||
|
Voltage is either too high or too low. |
Ensure the voltage corresponds to the device’s recommended range. |
||
|
The cooling air duct is obstructed by accumulated dust, leading to inefficient ventilation and motor cooling. |
Regularly clean and remove any debris or buildup from the air duct to ensure optimal airflow. |
||
|
Transmission Device |
Wear of transmission components, leading to increased friction (e.g., bearings, screws, etc.) |
Send to a professional manufacturer for repair. |
|
|
Lubrication oil levels being either excessive or insufficient can compromise heat dissipation efficiency. |
Periodically monitor and verify oil levels. Based on the assessment, either remove excess oil or replenish as necessary. |
||
|
The connection point between the power machine(engine) and the transmission device exhibits suboptimal geometric precision. |
Adhere to specified guidelines to clean and tighten the connection. If the condition remains unresolved, please engage a professional manufacturer for repair service. |
||
|
3. Operating Noise Excessive |
Noise (Continuos) |
Damaged bearings, worn gears or screws, insufficient lubricating oil. |
Send to a professional manufacturer for repair. |
|
Improper geometric accuracy at connection points. |
Detach the load, isolate the source of the noise in segments, then retighten folloing the guidelines. If there’s no improvement, consult professional repair services. |
||
|
Over-tightened belts or chains resulting in excessive radial loads. |
|||
|
Intermittent Noise (at a consistent frequency) |
Damaged gears or foreign objects causing obstructions. |
Send to a professional manufacturer for repair. |
|
|
Abnormal machining precision of the device itself. |
Report the issue to supplier and seek professional repair services. |
||
|
Misalignment in the concentricity of transmission components. |
Detach the load, identify the source of the noise by segments, then retighten ajs per guidelines. If no improvement, seek professional repair services. |
||
|
Irregular Rotational Noise (at variable frequencies) |
Contaminated lubricating oil, presence of foreign objects, or insufficient oil. |
Check the oil’s color, consistency, and levels. |
|
|
4 Excessive Operational Vibration |
Continuous Vibration |
Wear of gears and bearings. |
Send to a professional manufacturer for repair. |
|
Improper fixation or loosened screws. |
Re-inspect and ensure the connection surface screws are properly tightened. |
||
|
Misalignment in the concentricity of transmission components, or the joining surface wasn’t thoroughly cleaned during connection. |
Detach from the load, isolate the source of the vibration in segments, then clean and retighten following the guidelines. If the issue persists, consult professional repair services. |
||
|
5. Oil Leakage |
At the motor flange location and the shell joint surface |
Loosened screws at the joint surface. |
Retighten the screws and ensure the anti-loosening washers are correctly installed. If unable to address this personally, contact the manufacturer. |
|
Damaged or aged seals at the sealing area. |
Replace the seals. If replacement is not feasible personally, contact the manufacturer. |
||
|
Excessive anti-rust oil applied during rust prevention. |
Clean the oil stains from the suspected areas and then recheck. |
||
|
At the planetary reducer's output/input flange location and the shell joint surface. |
Loosened screws at the joint surface. |
Retighten the screws and ensure the anti-loosening washers are correctly installed. If unable to address this personally, contact the manufacturer. |
|
|
Damaged or aged seals at the sealing area. |
Replace the seals. If replacement is not feasible personally, contact the manufacturer. |
||
|
Excessive anti-rust oil applied during rust prevention. |
Clean the oil stains from the suspected areas and then recheck. |
||
|
Foreign objects or wear at the point of contact with the axle. |
Seek professional repair services and replace the oil seal. |
||
|
Oil seal not installed properly, inclined, or installed backwards. |
Replace the seals, If replacements is not feasible personally, contact the manufacturer. |
Conclusions:
Planetary reducers, with their distinct transmission characteristics, are extensively used in industrial equipment for transmitting power, altering power direction, and positioning. Precision planetary reducers are even more vital in industrial production as transmission devices. GearKo planetary reducers particularly excel in power transmission and positioning.
When equipment malfunctions during operation, not only identifying the root cause time-consuming, but repair durations can also vary depending on the nature of the fault. Downtimes can have a significant impact on productions. We hope the potential reasons and verification methods we’ve outlined above can assist you in reducing the time needed to identify and rectify issues.
If you encounter any challenges with reducers or face any complex issues, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We welcome the opportunity to address your concerns. Feel free to reach out to GearKo in Taiwan via phone or email.