2023.11.17
Core Components of GearKo Planetary Gearboxes: Types and Applications of Bearings

Bearings are a type of rolling element and a specialized term within mechanical components. They are commonly encountered in our daily lives, are used in vast quantities, and come in a multitude of types. Their function is to reduce frictional force during the relative rotation between machine parts and their axles, and to support the parts while maintaining the central position of the relative axles. Depending on the application and the direction of the load, different types of bearings are used. This article will provide a brief introduction to the deep groove ball bearings, angular contact ball bearings, tapered roller bearings, and needle roller bearings commonly used within GearKo planetary gearboxes.
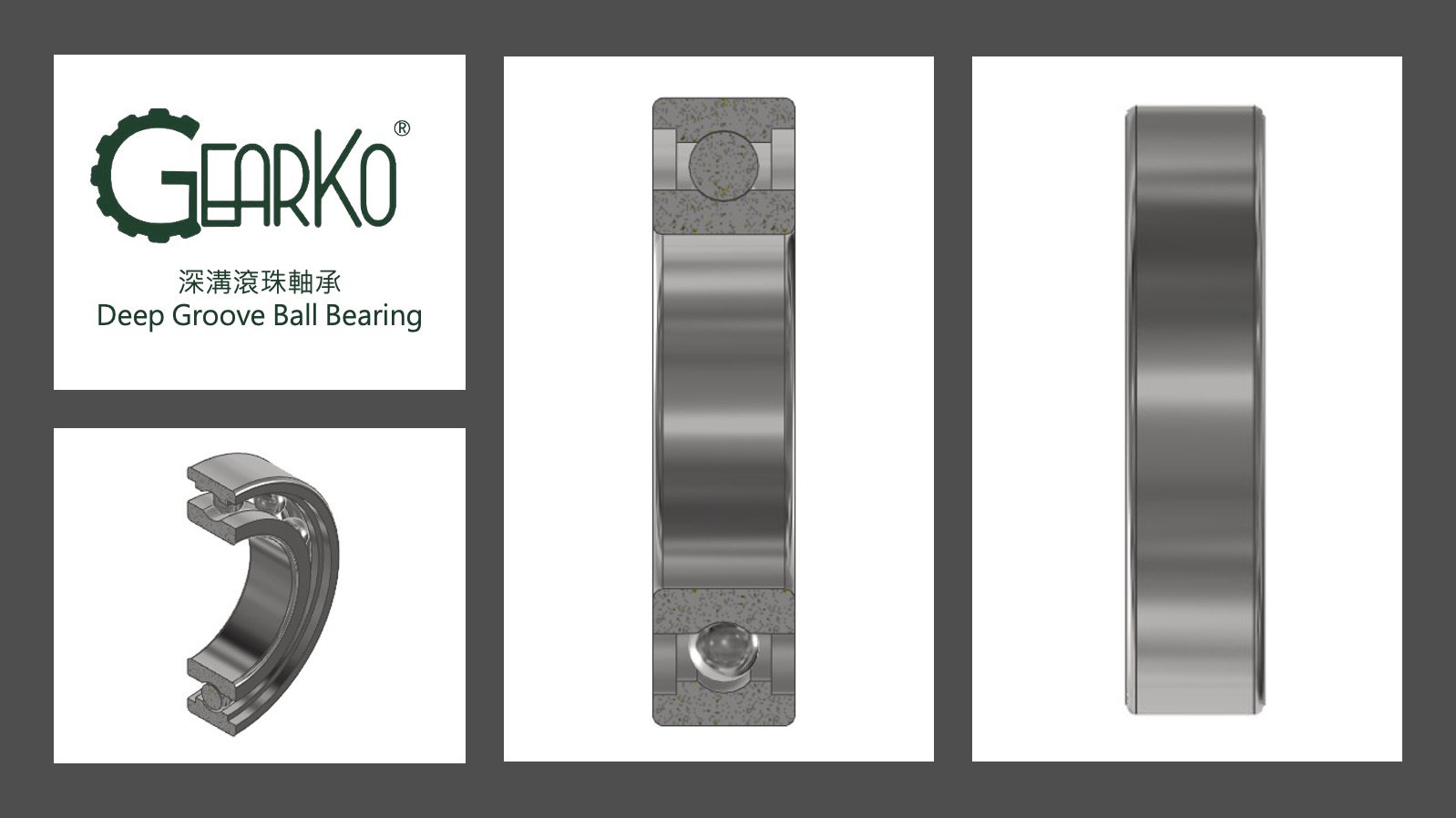

Deep Groove Ball Bearings
Deep groove ball bearings are the most common type of bearings found across various applications, capable of supporting moderate radial and axial loads. Their ball-shaped structure allows for high-speed rotation, low noise, minimal vibration, and reduced frictional torque. Deep groove ball bearings are equipped with dust covers on both the left and right outer sides. In addition to the open type, there are options with rubber seals and thin steel plates for enhanced protection.
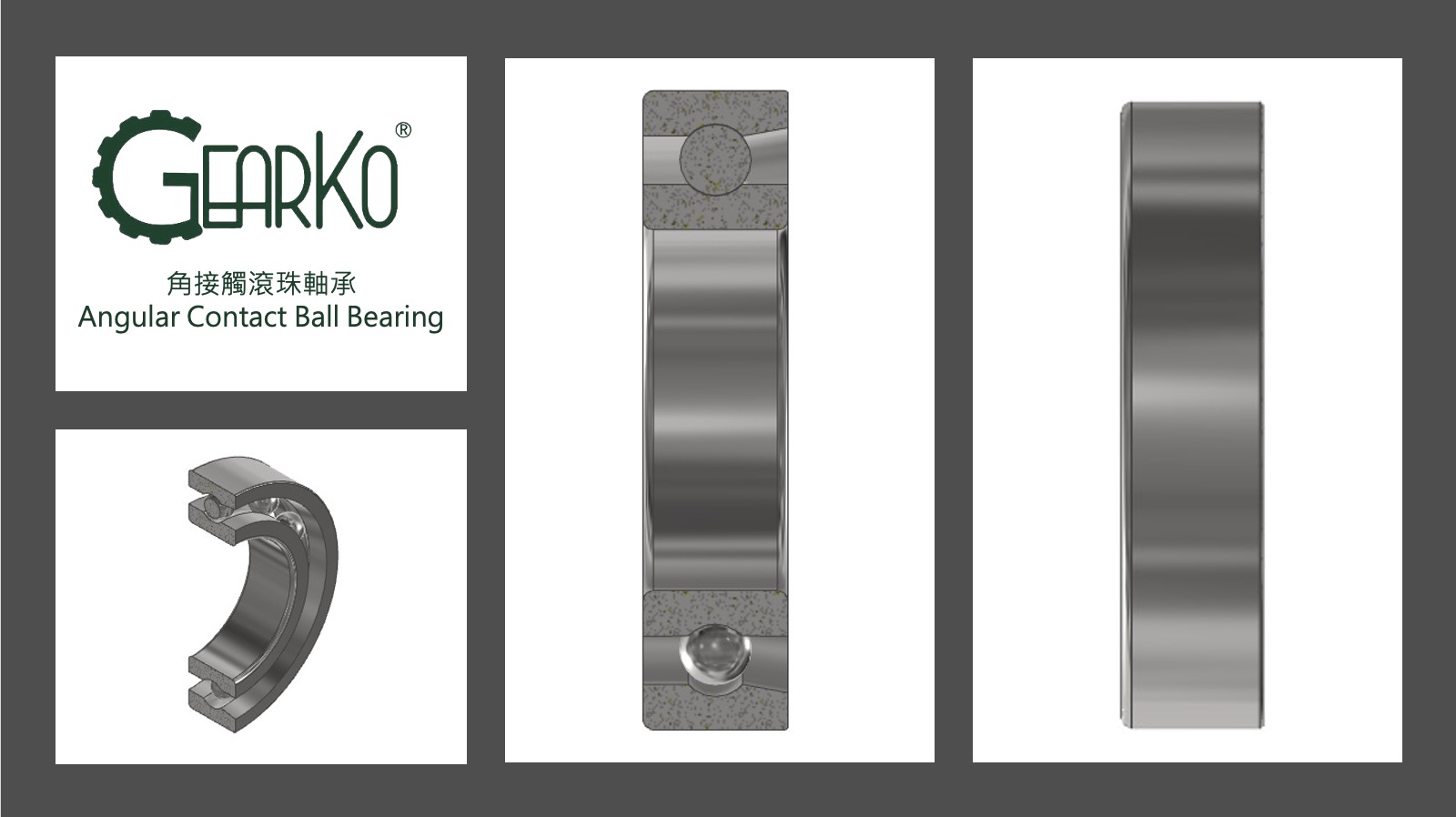

Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings are designed with varying contact angles to accommodate different operational conditions, typically at 15, 25, 30, or 40 degrees. These bearings have one side open at an angle, while the other side resembles a deep groove ball bearing. Their ball-shaped structure allows for high-speed rotation, low noise, low vibration, and reduced frictional torque. Upon axial non-open-end unilateral loading and radial loading, these bearings will exhibit axial separation. Therefore, they must be used in reversed pairs or sets. The bearing rigidity can be increased through the method of preloading adjustment, which is especially common in high-speed spindle applications.
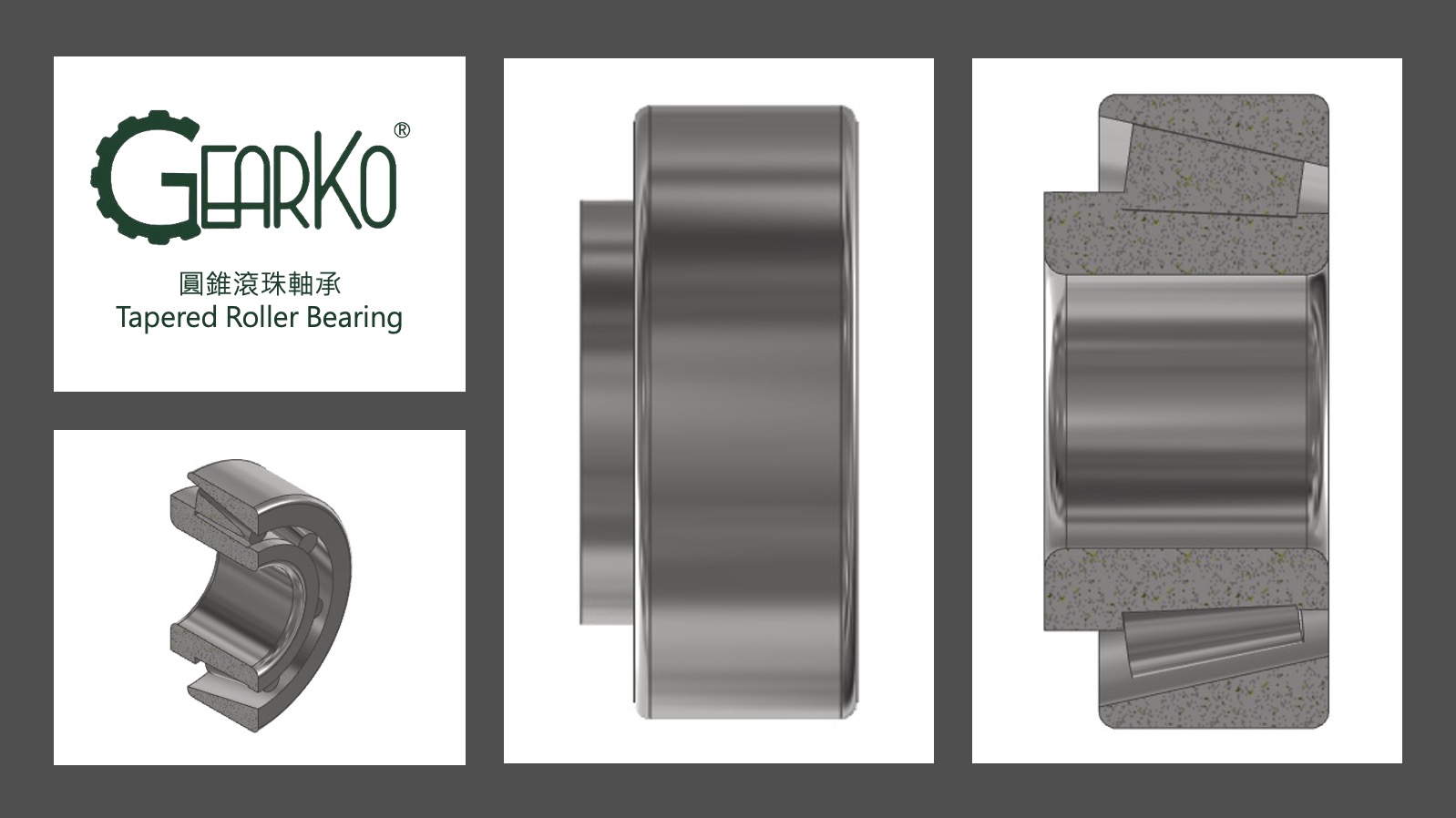
Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings, due to their conical structure, are characterized by high rigidity and high load capacity. Similar to angular contact ball bearings in their response to loads, these bearings will experience axial separation when subjected to axial loads on the non-open end side and radial loads. Therefore, they must be mounted in reversed pairs or in series. The rigidity can be enhanced by adjusting the preload to manage the clearance, which is a common practice for these types of bearings.
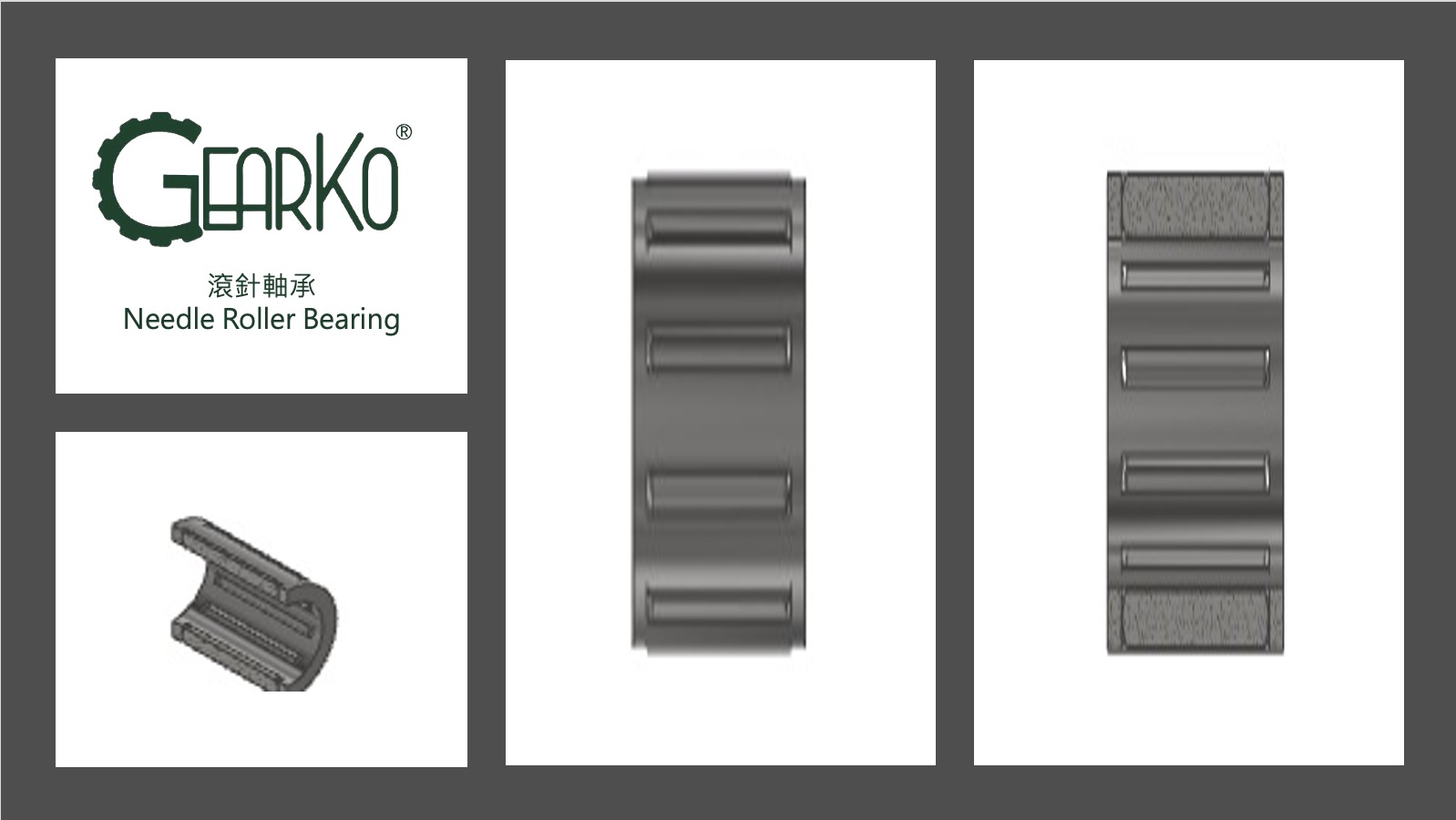
Needle Roller Bearings
Needle roller bearings consist of a multitude of high-precision needle rollers and a cage made of steel pins. They are characterized by their compact size, high rigidity, high load capacity, and superior resistance to radial movement and oscillation.
GearKo Gearbox Bearing Configurations for Each Series
|
Position Series |
Output End Bearing Type |
Intermediate Bearing Type |
Input End Bearing Type |
Notes |
|
GB/GE |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
|
|
GD/GHA |
Angular Contact Ball Bearings |
Angular Contact Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Tapered Roller Bearings Used in GD140 |
|
GF |
Tapered Roller Bearings |
Tapered Roller Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
|
|
GCB/GCE |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
|
|
GBR/GER |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
|
|
GDR |
Angular Contact Ball Bearings |
Angular Contact Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Tapered Roller Bearings Used in GDR140 |
|
GFR |
Tapered Roller Bearings |
Tapered Roller Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
|
|
GA/GAE |
Double Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
Deep Groove Ball Bearings |
|
The bearings used in GearKo gearboxes are all from major manufacturers, ensuring quality. Customers can specify the precision and clearance as required. If there are any issues, please contact GearKo, and we will provide you with comprehensive technical consulting services.