2023.06.16
Delving into the Gear World: Exploring the Key Role of Planetary Gearboxes
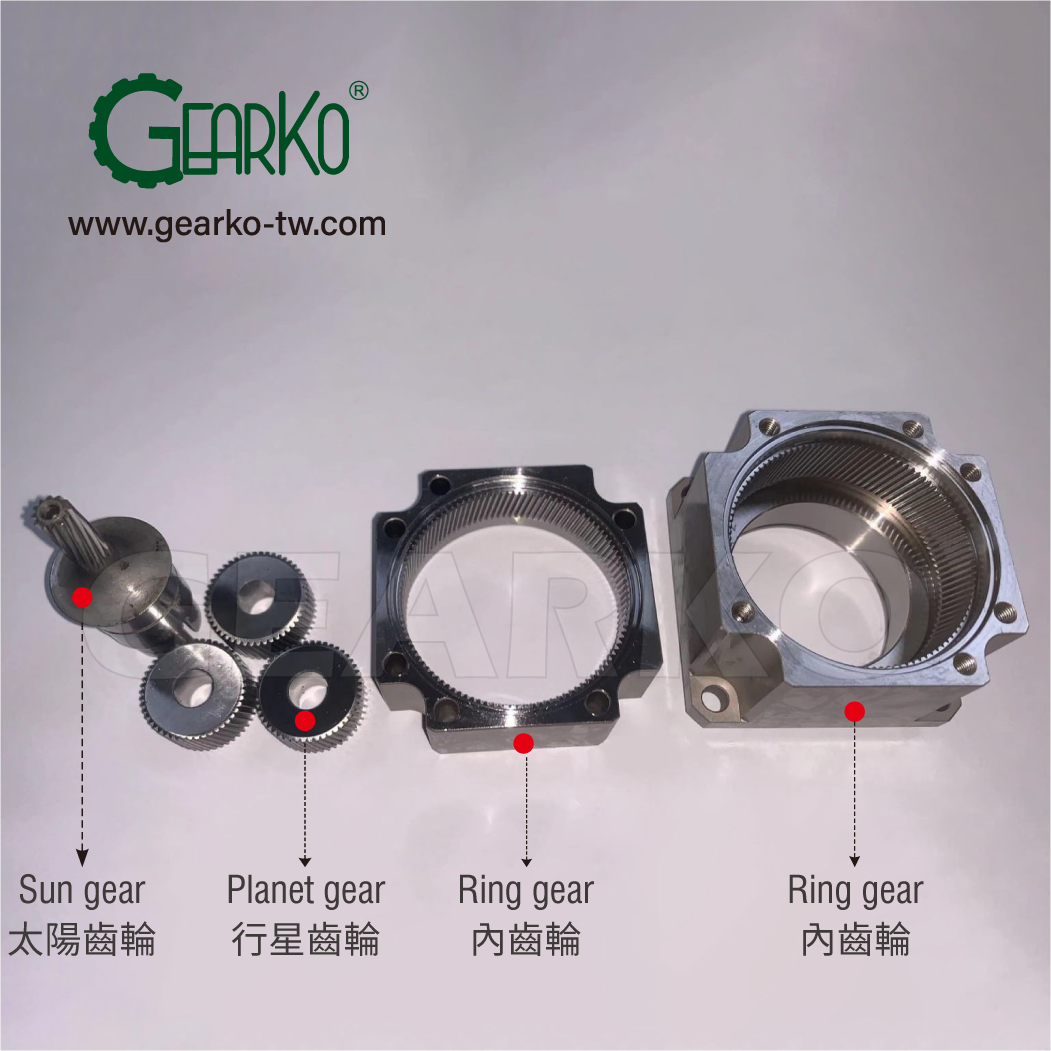

Gears are indispensable components in mechanical power transmission and play a crucial role in the mechanism of planetary gearboxes. They have a rich historical background and a wide range of applications. The use of gears can be traced back to ancient times, with evidence found in the writings of Greek philosopher Aristotle and sketches by the Italian Renaissance genius Leonardo da Vinci.
Gears are extensively employed in various industries, from simple transmissions in early times to sophisticated mechanical power transmission systems in modern times. They are vital in everyday life and industrial equipment, providing essential support in numerous consumer and industrial products.
The transmission principle of gears is based on their meshing engagement. By controlling the input gear's speed and torque, we can precisely adjust the output gear's speed, torque, and direction of motion. Gear transmission offers advantages such as high efficiency, reliability, and low power loss, making it an indispensable choice in the field of mechanical power transmission. GearKo excels in maximizing the strength and application of gears in planetary gearboxes.
Gears have standardized dimensions represented by module (M) or diametral pitch (DP), ensuring correct meshing in gear transmission. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) uses module as a representation, such as M1, M5, M10, where a larger number indicates larger gears and a smaller number indicates smaller gears. In countries that use the imperial system, diametral pitch (DP) is used. For example, DP24, DP32 represents the number of teeth for a gear with a pitch diameter of 1 inch, with a higher number indicating smaller gears.
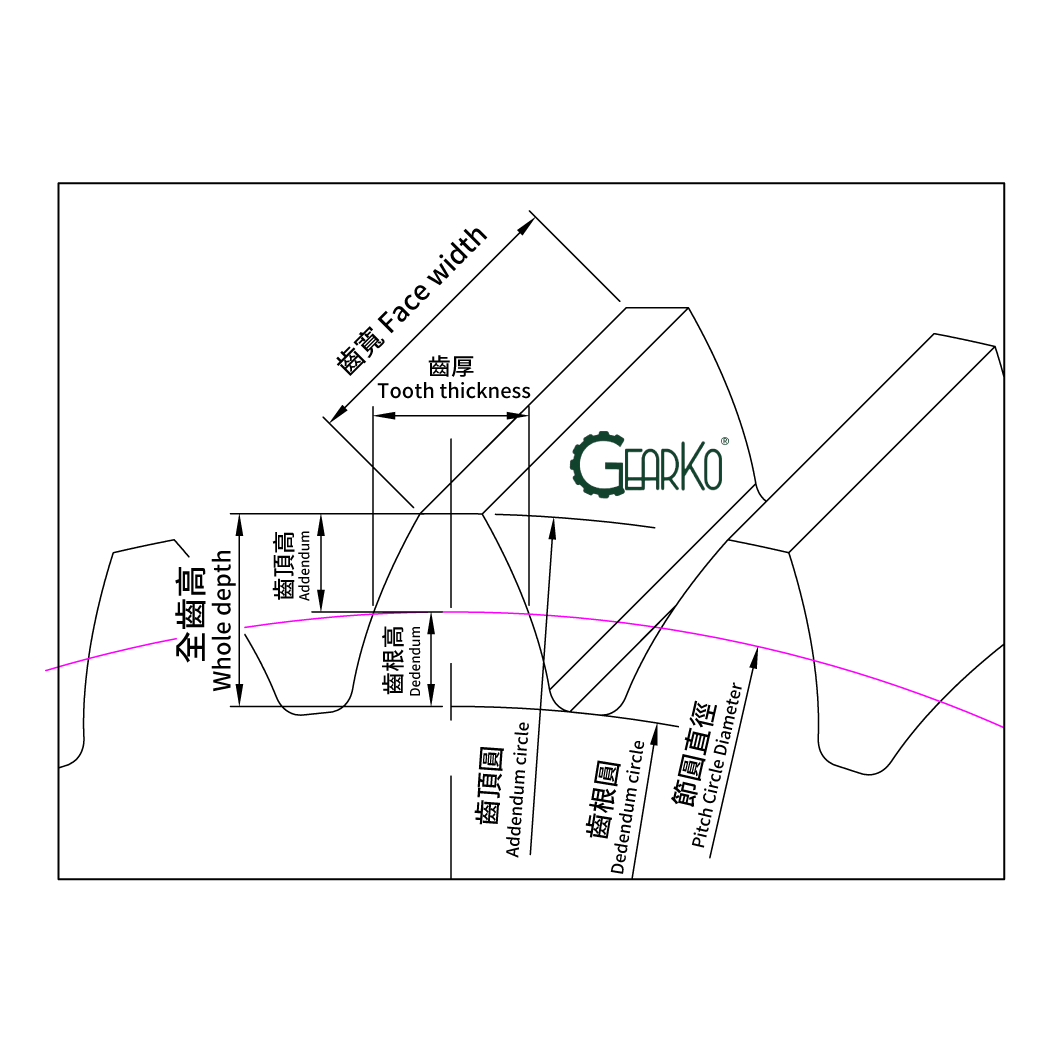
For more detailed information on gears, you can refer to the external resources provided by KHK Gears:
Gear ABC Introduction (Traditional Chinese): https://www.khkgears.co.jp/tw/gear_technology/pdf/gearabc_a.pdf
Gear ABC Basics (Traditional Chinese): https://www.khkgears.co.jp/tw/gear_technology/pdf/gearabc_b.pdf
Gear ABC Introduction (English): https://khkgears.net/pdf/gearabc_a1.pdf
Gear ABC Basics (English): https://khkgears.net/new/gear_knowledge/abcs_of_gears-b/